The Art of Repurposing Buildings
The adaptive reuse of buildings—the process of repurposing structures for viable new uses—is an increasingly popular trend in the areas of architecture and urban development. It is a strategy that not only breathes new life into vacant or underutilized spaces but also positively impacts the social fabric of a community and advances sustainability. A compelling example of this transformative process is EAPC Architects Engineers’ recent project in rural Minnesota, Essentia Health’s Ambulatory Care Center.
THE EAPC team masterfully converted a once thriving Pamida store into a state-of-the-art healthcare hub. The retail building, formerly the bustling heart of commerce and a symbol of the industrious local community, has metamorphosed into a beacon of modern healthcare. Situated on the city’s main artery, the revamped facility is a testament to the innovative combination of traditional medical practices with a hospitality element, placing paramount importance on patient comfort and tranquility.

“Essentia Health approached EAPC with the intricate task of converting a large retail space into a functional outpatient clinic, explained EAPC Senior Architect, Matt Becker. “Despite the complexities, our design team embraced the challenge, demonstrating adaptability and aptitude in transforming unconventional spaces into efficient healthcare facilities.”

The transformation of this 1980s building is a striking example of how adaptive reuse can reinvigorate a space. What once stood as a silent, empty shell is now a vibrant center of wellness, deftly incorporating the novel ‘onstage’ and ‘offstage’ healthcare model.
The ‘onstage’ area, representative of the forefront of patient care, is a dynamic space where medical professionals and patients engage under the Patient-Centered Medical Home model. This model places strong emphasis on open dialogue, holistic care, and serene surroundings, all encapsulated in a space that was previously a retail environment.
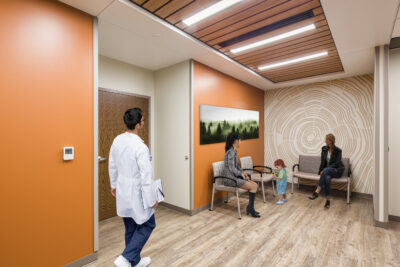
A standout element in this transformative design is the use of intuitive wayfinding components. The floors serve as a subtle guide, directing patients and families throughout the facility, while the continuous wood ceiling creates a sense of flow and direction, simultaneously infusing a warm, natural aesthetic to the interior.
On the flip side, the ‘offstage’ zone functions as the operational hub where professionals plan and strategize patient care. This region signifies a shift from isolated medical setups to an integrated, collaborative layout promoting teamwork, demonstrating that adaptive reuse can also transform operational dynamics in healthcare settings.
The introduction of innovative pod spaces for registered nurses is a key feature of this new layout. These areas enhance workflow, allow for an unobstructed cohesion between ‘onstage’ and ‘offstage’ areas, and encourage care delivery to function as a well-orchestrated team.
“Achieving a successful onstage/offstage design meant meticulously balancing patient and provider spaces within a fixed building footprint. It wasn’t just about satisfying spatial needs, but also about ensuring smooth movement for everyone. Careful planning was critical for an efficient and effective layout,” added Becker.
The Essentia Health project serves as an inspiring case study demonstrating the potential of adaptive reuse in creating community-focused, sustainable healthcare facilities. It emphasizes that the transformation of spaces isn’t just about physical change, but about redefining their function and impact on the community.
Adaptive reuse projects like this serve as a beacon of hope, promising to deliver care and comfort for generations. They underline the potential in repurposed spaces and highlight the significance of community strength and dedication. As we look towards creating a sustainable, functional, and inclusive future, adaptive reuse of buildings, as exhibited by Essentia Health, presents an exciting and promising path forward.